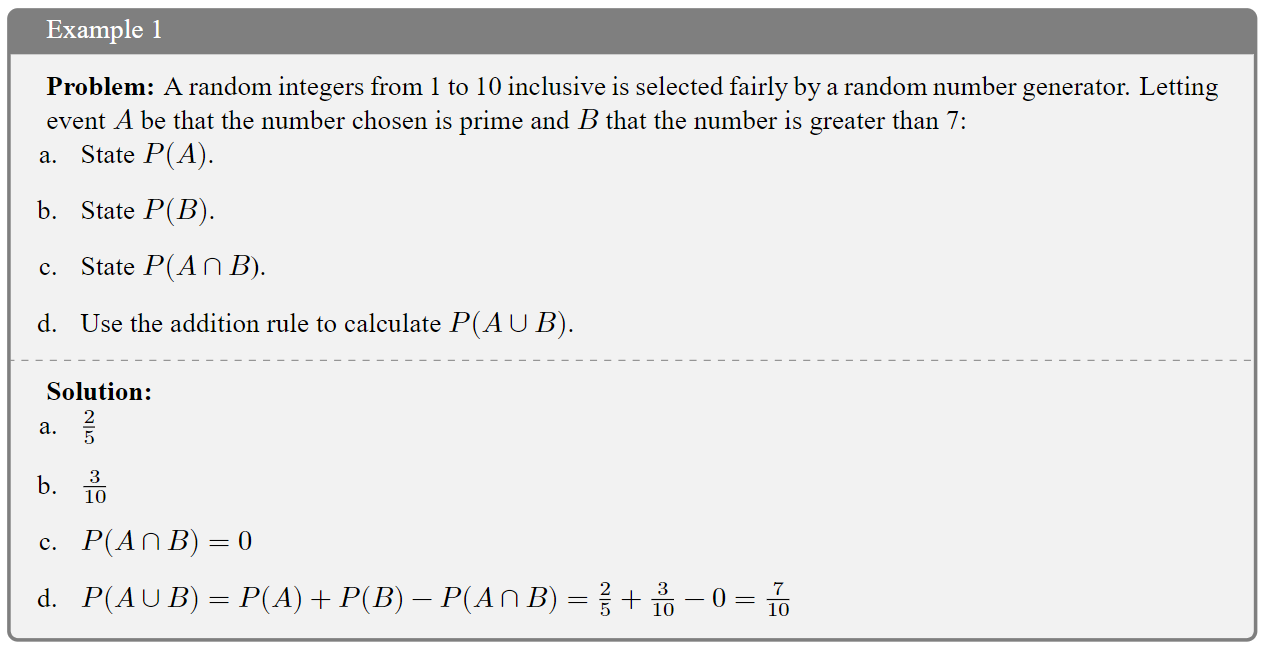
1.6 The Addition Rule
A rule for calculating the union of events can now be derived by considering its representation on a Venn diagram.

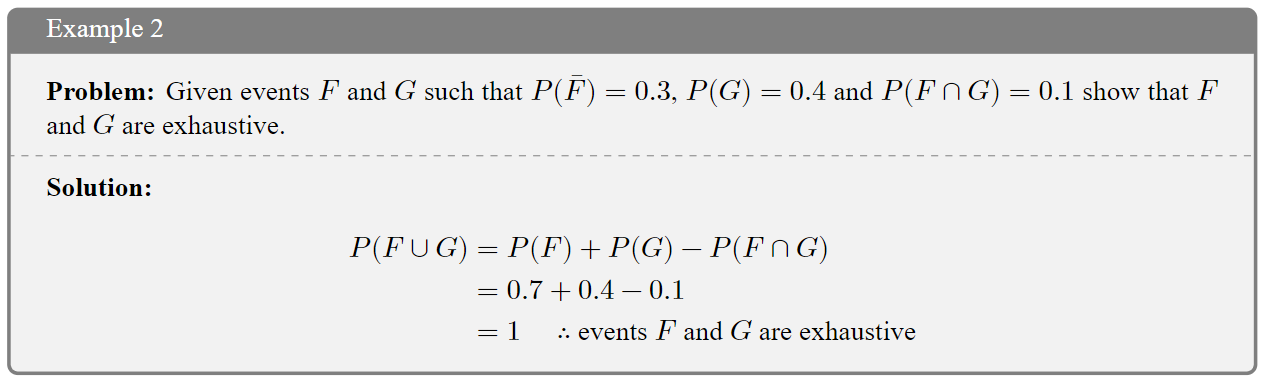
The rule above is valid for all events \(A\),\(B\), but simpler verions can be used when certain conditions are satisfied. Recall that for mutually exclusive events, the probability of the intersection is 0 (impossible), and for exhaustive events the probability of the union is 1 (certain).
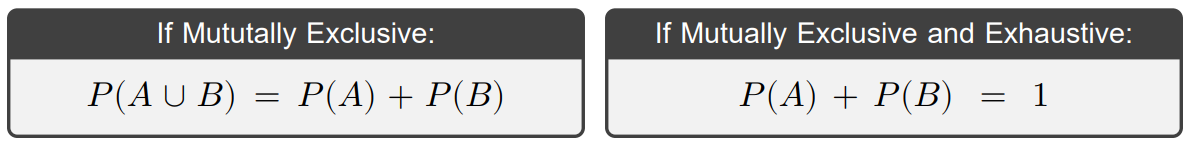
To work with probability rules, it helps to carefully notate the information known from the question, paying attention to words such as exhaustive and mututally exclusive, then consider which rule may connect the known probabilities with the probabilities being asked for.