3.2 Bright Field Microscopy
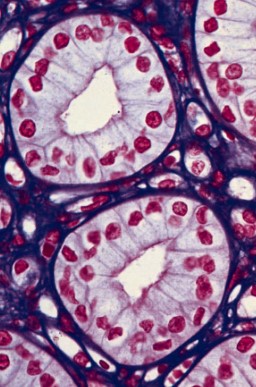
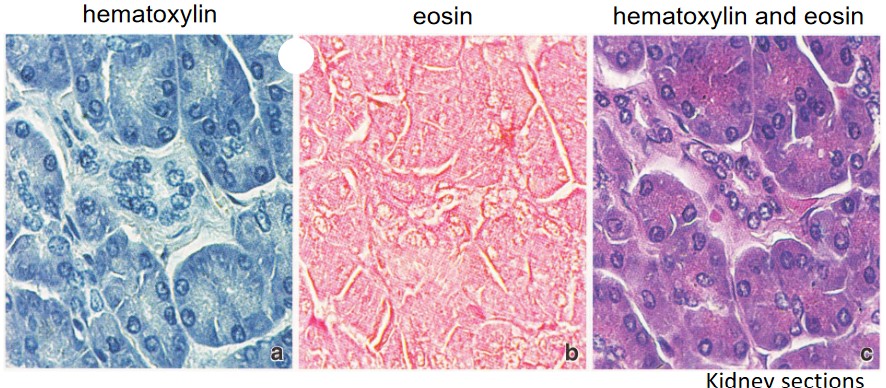
Figure 3.7: H&E Stained Kidney Cells Viewed with Bright Field Microscopy
In this kind of microscopy, bright light is used to visualize samples. Such visualizations are based on the absorption of certain wavelengths of light.
3.2.1 Preparing a Sample for Light Microscopy
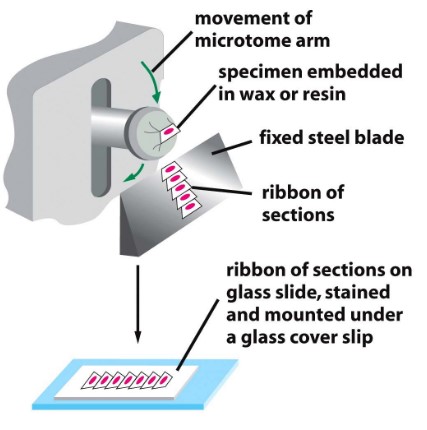
Figure 3.8: A Microtome Machine
There are three main steps:
Fixation
This kills and preserves cells. Formaldehyde is commonly used.
Embedding and Sectioning
The fixed tissue is dehydrated and embedded in hot wax or resin.
This practice increases the mechanical strength of the tissue for sectioning (about 5 - 15 micrometers thick).
Staining
This rehydrates the sample - various staining techniques can be used to reveal cellular and subcellular structures (e.g., organic dyes, H&E staining, etc).