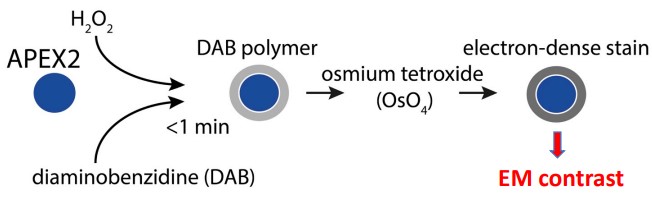
9.3 Protein Localization in Conventional TEM
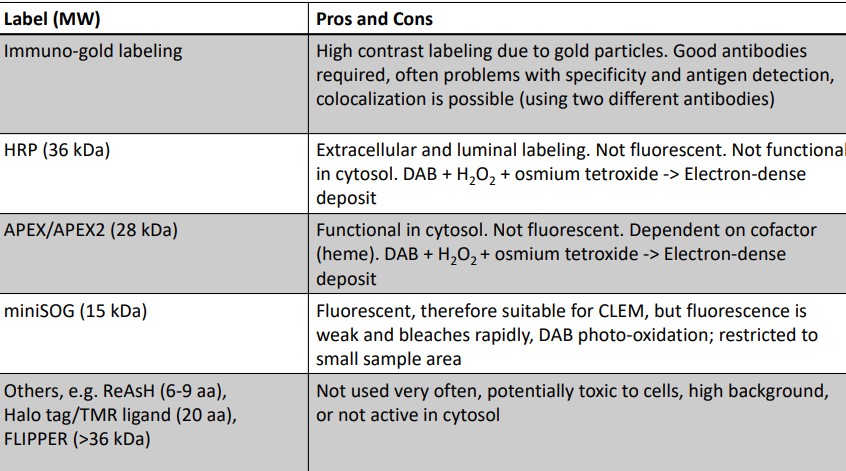
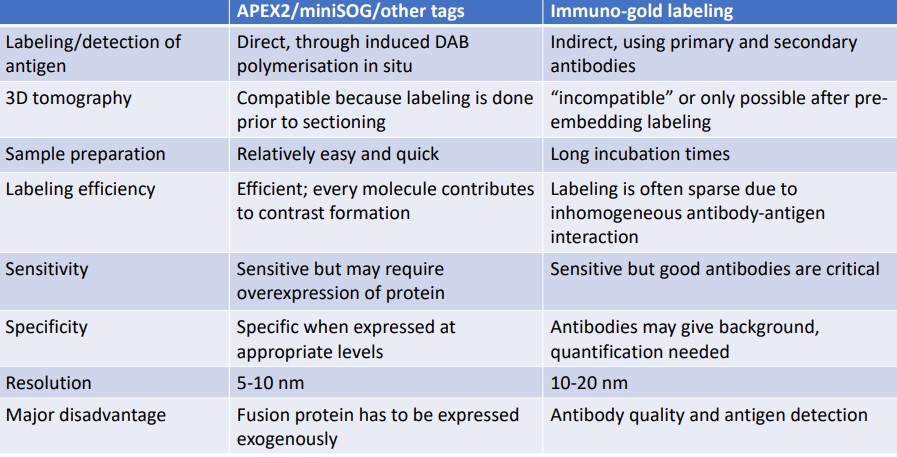
Figure 9.11: Pros and Cons in Protein Labelling Methods
The above figure shows some pros and cons of some common protein localization methods in a conventional TEM.
9.3.1 Immuno-gold EM
This is the labeling of proteins with specific antibodies (much like in fluorescence light microscopy):
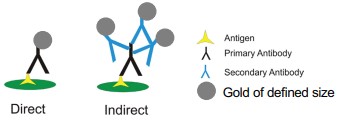
Figure 9.12: Gold-Labeling Proteins
Here, gold is attached to an a(n) (in)direct antibody. Colocalization analysis is also possible with two different antibodies and different gold particle sizes.
9.3.1.1 Labeling Golgi Proteins
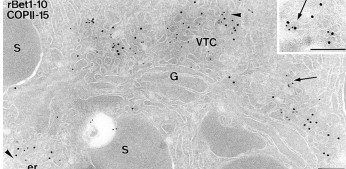
Figure 9.13: Immuno-Labeling of a Post-Embedded Protein
Labelling in post-embedded proteins is generally carried out on sections (i.e., Tokuyasu sections) - many different combinations of antibodies can be carried out on one sample. No detergents are also needed, and antibodies can only detect antigens that are exposed to the surface of the section.
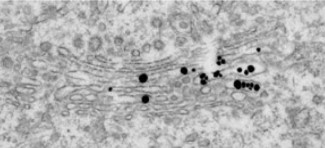
Figure 9.14: Immuno-Labeling of a Pre-Embedded Protein
Pre-embedded proteins are labelled inside a cell. Because of this, permeabilization with proteins is needed; silver enhancements are also required to detect small gold particles.