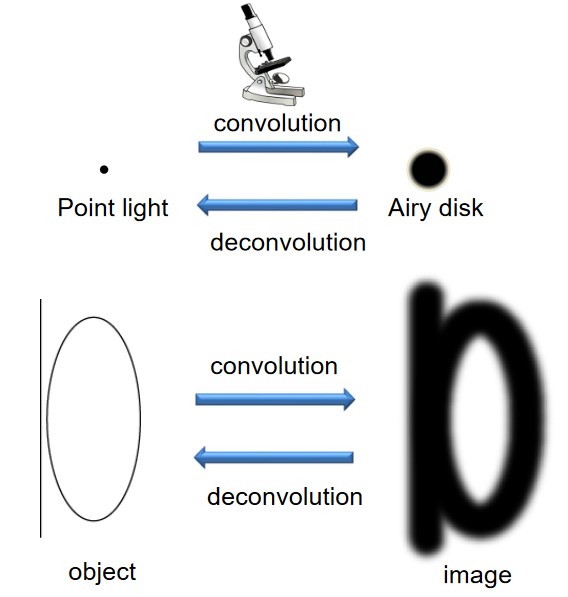
3.4 Image Formation
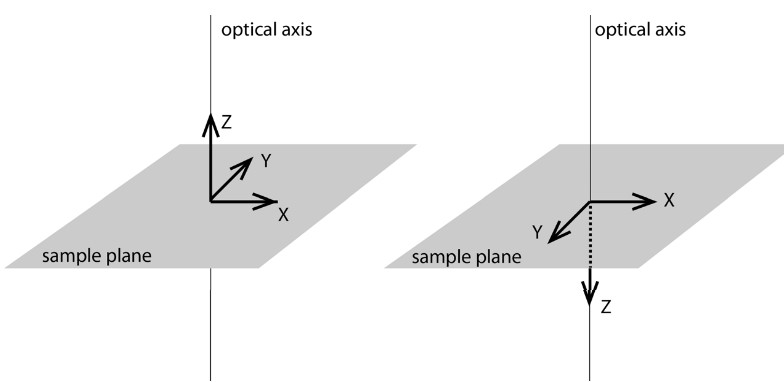
Figure 3.12: Planes in Microscopy
The xy plane in microscopy is the sample plane; the ‘z’ axis is along the optical axis.
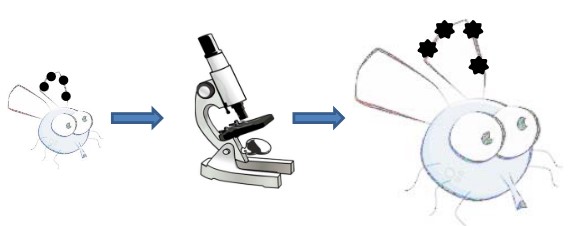
Figure 3.13: Image Formation in Microscopy
Image formation is step-wise process in microscopy: if one knows the image of a geometric point, then one also knows the image of the object.
3.4.1 Image of a Point Light Source
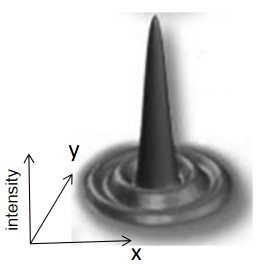
Figure 3.14: A PSF
Light diffracts when it passes through a microscope; the three-dimensional image of an infinitely small light source is called the Point Spread Function (i.e., PSF).
3.4.2 Rayleigh Criterion
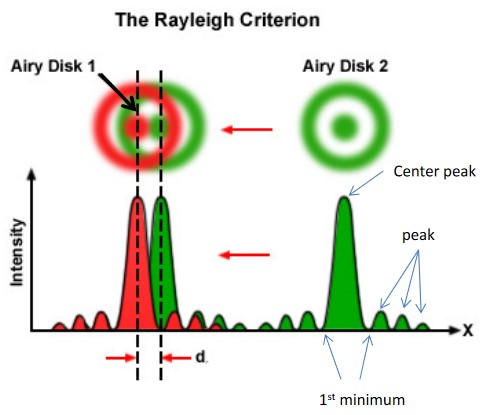
Figure 3.15: Rayleigh Criterion
The spatial resolution is the smallest distance between two point light sources. The resolution is highly subjective.
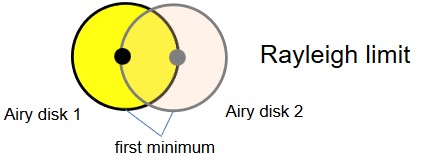
The Rayleigh limit is the center of the first airy disk that coincides with the circumference of the second airy disk.
The resolution is the radius of an airy disk.
3.4.3 Micoscope Spatial Resolution
The spatial resolution xy of a microscope d is:
d=1.22λNAcondenser+NAobjective
In most cases, NAcondenser=NAobjective, so:
d=0.61λNA
The resolution between along the z-axis of a microscope is about 2d. Light microscopy has a resolution limit of about 200 nm.